How to operate hydraulic test fittings safely?
Hydraulic test fittings are essential components in hydraulic systems, widely utilized in fields such as construction machinery, industrial equipment, aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and oil and gas.
Their primary role is to measure and monitor system pressure, ensuring stable operation and safety. However, improper use or poor maintenance can lead to system failures and potentially severe safety incidents.
Therefore, mastering the safe operation guidelines for pressure measuring joints is crucial. This paper delves into the correct operation and maintenance practices for pressure measurement joints to ensure their safety and reliability in practical applications.

1. Basic structure and operation principle of pressure-measuring connectors
A pressure measuring fitting typically comprises a body, seals, and connecting components. Its function is to detect pressure fluctuations within a hydraulic system, delivering real-time data that allows operators to monitor and adjust the system’s performance accordingly. Hydraulic test fittings are engineered for optimal tightness and stability in high-pressure environments, effectively preventing fluid leaks and potential system failures.
2. Basic principles of safe operation
2.1 Knowledge of equipment
Before operating a pressure measuring fitting, it’s essential to thoroughly understand its structure, working principles, and operating instructions. Familiarize yourself with the equipment’s performance parameters, including maximum working pressure, temperature range, and suitable media. This knowledge ensures that the equipment operates within its design limits, preventing any operational issues.
2.2 Wear appropriate protective equipment
Always utilize suitable protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing, when operating pressure-measuring fittings. This gear is crucial for preventing injuries from high-pressure fluid leaks and ensures operator safety.
2.3 Checking the status of equipment
Before operation, thoroughly inspect the condition of the pressure measuring fitting to ensure there are no signs of damage or wear. Pay special attention to the seals, which must be intact to prevent leaks. Additionally, check the connecting parts for tightness to ensure a secure and reliable connection.

3. Safe practices for installation and dismantling
3.1 Installation of hydraulic test fittings
-Selecting an Appropriate Location: Choose a suitable spot within the hydraulic system for installation to ensure the measurement point accurately reflects the system’s operating pressure.
– Cleaning Connecting Parts: Prior to installation, thoroughly clean both the pressure measuring fitting and the system’s connecting parts to remove any impurities or contaminants that might compromise the seal.
– Using the Right Tools: Employ the correct tools for installation and avoid applying excessive force to prevent damage to the fittings or connecting components. Adhere to the equipment manufacturer’s installation instructions to ensure proper setup.
3.2 Disassembly of hydraulic test fittings
– Pressure Relief: Before removing the pressure measurement fitting, ensure that the system is fully depressurized to eliminate any residual pressure and prevent injuries from fluid discharge.
– Equipment Protection: During disassembly, carefully protect the pressure measurement fittings and connecting parts from impacts and damage. After removal, store the connectors properly to prevent contamination and damage.
4. Safety precautions in operation
Monitoring System Pressure: During operation, continuously monitor the system pressure in real-time to ensure it remains within a safe range. Avoid overpressure conditions to prevent damage to the pressure measuring fitting and the hydraulic system.
Avoiding Sudden Pressure Changes: Prevent sudden pressure changes during operation to avoid shocks to the pressure measuring fitting and the hydraulic system. Adjust the system pressure gradually to ensure a smooth transition.
Compliance with Operating Procedures: Adhere strictly to the operating procedures and avoid unauthorized actions. If any abnormal conditions arise during operation, stop immediately, identify the cause, and address it to ensure system safety.

5. Safe practices for maintenance and upkeep
5.1 Regular inspection and maintenance
– Inspection of seals: Regularly inspect the seals of the pressure measuring joints, and replace them in time if they are found to be aged or damaged. Select high-performance sealing materials to improve the sealing effect and service life.
– Cleaning the equipment: Clean the pressure measurement fitting regularly to prevent dust, impurities and corrosive substances from entering the inside of the fitting. Use appropriate cleaning agents and tools to ensure that both the inside and outside of the fitting are kept clean.
5.2 Lubrication and fastening
– Lubrication: For pressure-measuring fittings that require frequent operation, lubricate regularly to reduce wear and operating resistance. Select a suitable lubricant and avoid lubricants that are harmful to the sealing material.
– TIGHTENING: Periodically check the tightness of the joints to ensure that they are securely connected. For loose joints, tighten them with appropriate tools to prevent leakage and system instability.
5.3 RAM
– Maintenance records: Detailed records of each maintenance and servicing, including inspection items, problems found and treatment measures. Through the maintenance records, the history of equipment use can be traced, potential problems can be found and dealt with in a timely manner.
– File management: Establish a file management system for the pressure measuring joints, keep the technical data, operation instructions and maintenance records of the equipment, etc., so as to facilitate the daily management and maintenance.
6. Emergency response measures
Regular Inspection and Maintenance:
- Seal Inspection: Regularly examine the seals of pressure measuring joints and promptly replace any that are aged or damaged. Use high-performance sealing materials to enhance sealing effectiveness and extend service life.
- Equipment Cleaning: Routinely clean the pressure measuring fitting to prevent dust, impurities, and corrosive substances from entering. Use appropriate cleaning agents and tools to ensure both the interior and exterior of the fitting remain clean.
Lubrication and Fastening:
- Lubrication: For pressure measuring fittings that require frequent operation, lubricate regularly to minimize wear and operational resistance. Choose a suitable lubricant and avoid those that could harm the sealing material.
- Tightening: Periodically check the tightness of the joints to ensure secure connections. Use appropriate tools to tighten any loose joints, preventing leaks and system instability.
Record and Maintenance (RAM):
- Maintenance Records: Keep detailed records of each maintenance session, including inspection items, identified issues, and corrective actions taken. These records help trace the equipment’s usage history and identify potential problems early.
- File Management: Establish a file management system for pressure measuring joints, maintaining technical data, operation instructions, and maintenance records. This system facilitates daily management and maintenance activities.
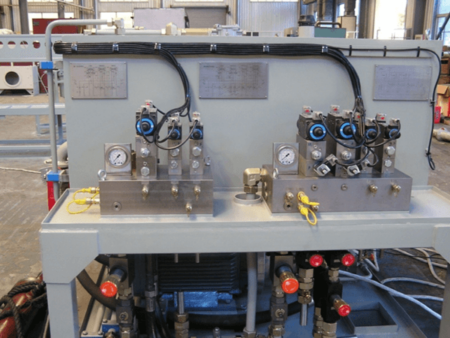
7. Case studies
Case 1: Safe Operation of hydraulic test fittings in a Chemical Plant
In a chemical plant, numerous hydraulic test fittings were utilized within the hydraulic system. An incident occurred when an operator failed to perform the necessary pressure relief operation, resulting in a high-pressure liquid spray during disassembly and causing injury.
Following an investigation, the chemical plant developed detailed operating procedures and provided comprehensive training to the operators. These measures significantly improved the operational safety of the pressure measuring joints and prevented similar incidents from occurring.
Case 2: Maintenance of pressure-measuring fittings at a manufacturing company
A manufacturing company employed high-pressure hydraulic test fittings in its hydraulic press equipment. Due to neglect in timely maintenance and repair, the seals of the pressure-measuring fittings deteriorated and became damaged, leading to system leaks.
To address the issue, the company took the following actions: replaced all deteriorated seals with high-performance sealing materials; regularly inspected and cleaned the pressure-measuring fittings to ensure optimal condition; and trained operators to enhance their maintenance and operation skills. These measures effectively resolved the leakage problem and improved both the operational efficiency and safety of the equipment.
Hydraulic test fittings are crucial components in hydraulic systems, and their safe operation and maintenance are directly linked to the stability and safety of the system. By understanding the equipment’s structure, wearing appropriate protective gear, checking the equipment’s condition, installing and removing it correctly, monitoring system pressure, avoiding sudden pressure changes, adhering to operating procedures, conducting regular inspections and maintenance, maintaining thorough records and files, and implementing emergency response measures, you can ensure the safety and reliability of pressure-testing fittings in practical applications.
Real-world case studies demonstrate that following scientific operation and maintenance protocols not only enhances the service life and performance of pressure measuring joints but also effectively prevents safety incidents. Therefore, attention to the safe operation specifications of pressure measuring joints is essential for ensuring the stable operation of hydraulic systems and the safety of operators.

